Diatomic Molecules-a molecule containing two atoms like Cl2 for example.
Bonding- Force of attraction between two atoms.
Ions- Charged particles made from an atom by the gain or loss of electrons to gain stability like the sodium atom will lose one electron to achieve a noble gas arrangement 2,8 (before 2,8,1). This will have a sign Na+ (+ sign on top)
Lattice- a regular three-dimensional arrangement of atoms, molecules or ions in a crystalline solid.
Metallic Bonding
 This happens only in metals. Here the atoms in the metals lose the electrons from their outershell. These electrons become delocalized and the atoms become positively charged ions. This hence forms an electrostatic force between the regular array of +ve metal ions and the sea of delocalized electrons within a metal solid.
This happens only in metals. Here the atoms in the metals lose the electrons from their outershell. These electrons become delocalized and the atoms become positively charged ions. This hence forms an electrostatic force between the regular array of +ve metal ions and the sea of delocalized electrons within a metal solid.
Metallic bonding is the strong attraction between closely packed positive metal ions and a 'sea' of delocalized electrons.
Non-metals + Non-metals= Covalent Bonding

(The two chlorine ions can be written as 2 then the chlorine ion structure as shown, these type of diagrams are always asked in the exam so better practice them like the one above, just show the outershell in these diagrams.)
Formulas of poly atomic ions
Really important to learn these formulas of ions in writing formulas of substances.
Summary
More is on the way... keep checking :)
Bonding- Force of attraction between two atoms.
Ions- Charged particles made from an atom by the gain or loss of electrons to gain stability like the sodium atom will lose one electron to achieve a noble gas arrangement 2,8 (before 2,8,1). This will have a sign Na+ (+ sign on top)
Lattice- a regular three-dimensional arrangement of atoms, molecules or ions in a crystalline solid.
Metallic Bonding
 This happens only in metals. Here the atoms in the metals lose the electrons from their outershell. These electrons become delocalized and the atoms become positively charged ions. This hence forms an electrostatic force between the regular array of +ve metal ions and the sea of delocalized electrons within a metal solid.
This happens only in metals. Here the atoms in the metals lose the electrons from their outershell. These electrons become delocalized and the atoms become positively charged ions. This hence forms an electrostatic force between the regular array of +ve metal ions and the sea of delocalized electrons within a metal solid.Metallic bonding is the strong attraction between closely packed positive metal ions and a 'sea' of delocalized electrons.
- The delocalized electrons can move freely therefore metals can conduct electricity.
- This electrostatic attraction is so strong that metals have high mp and bp.
- The +ve ions are arranged in layers which can slip over each other making metals malleable and ductile.
- Metallic bonding results in giant metallic lattices.
- Non-metals combine together by sharing pairs of electrons. This is known as a covalent bond. This holds the atoms together.
- Groups of atoms bonded together in this way is called molecules
- They don't have any free electrons or ions so they don't conduct electricity.
- This covalent bond is weak and can be easily broken, therefore covalent compounds normally occur as liquids or gases at rtp like chlorine, hydrogen and water.
- Group IV oxides (except carbon dioxide) makes giant molecular lattices like silicon (IV) oxide. These lattices have many strong covalent bonds which make make their melting points very high since a lot of energy is needed to break all of these bonds.
- Group V,VI, VII oxides and CO2 form simple molecular lattice which is simple molecules. These have low melting points since they have less bonds to break.

(The two chlorine ions can be written as 2 then the chlorine ion structure as shown, these type of diagrams are always asked in the exam so better practice them like the one above, just show the outershell in these diagrams.)
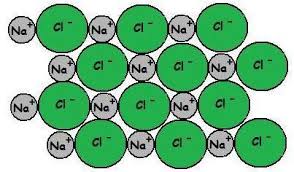
- An ionic bond is formed between non-metals and metals.
- The metal loses electrons to become a positive ion to attain noble gas arrangement and the non-metal becomes a negative ion by gaining those electrons.
- So there is a strong electrostatic force between the positive and negative ions. This is the ionic bond.
- Ionic bonds needs a lot of energy to break, therefore ionic compounds have high melting points. They are usually solid at rtp like NaCl (table salt).
- Ionic compounds conduct electricity only when they are molten or dissolved in water, not as a solid. In solids the ions cannot move therefore cannot conduct electricity. Yes, ions conduct electricity in ionic compounds.
- Ionic bonding results in ionic lattices a regular array of alternating +ve and -ve ions like in NaCl.
Really important to learn these formulas of ions in writing formulas of substances.
Valency
|
Simple Metal Ions
|
Simple non-metallic ions
|
Polyatomic ions
|
||
+ve
|
+ve
|
-ve
|
+ve
|
-ve
|
|
1
|
Sodium Na+
Potassium K+
Silver Ag+
Copper (I) Cu+
|
Hydrogen H+
|
Hydride H-
Chloride Cl-
Bromide Br-
Iodide I-
|
Ammonium NH4+
|
Hydroxide OH-
Nitrate NO3-
Hydrogencarbonate HCO3-
|
2
|
Magnesium Mg2+
Calcium Ca2+
Zinc Zn2+
Iron (II) Fe2+
Copper (II) Cu2+
|
Oxide O2-
Sulphide S2-
|
Sulphate SO42-
Carbonate CO32-
|
||
3
|
Aluminium Al 3+
Iron (III) Fe3+
|
Nitride N3-
|
Phosphate PO43-
|
||
Summary
More is on the way... keep checking :)


i love this! thank youuuuuuuu so much
ReplyDeleteMetal Bonded Diamond Wheels with Supreme Abrasive are like super-tough cutting champions! The strong metal glue holds onto Supreme Abrasive diamond bits perfectly, letting them slice through concrete, stone, and ceramics like a hot knife through butter.
ReplyDelete