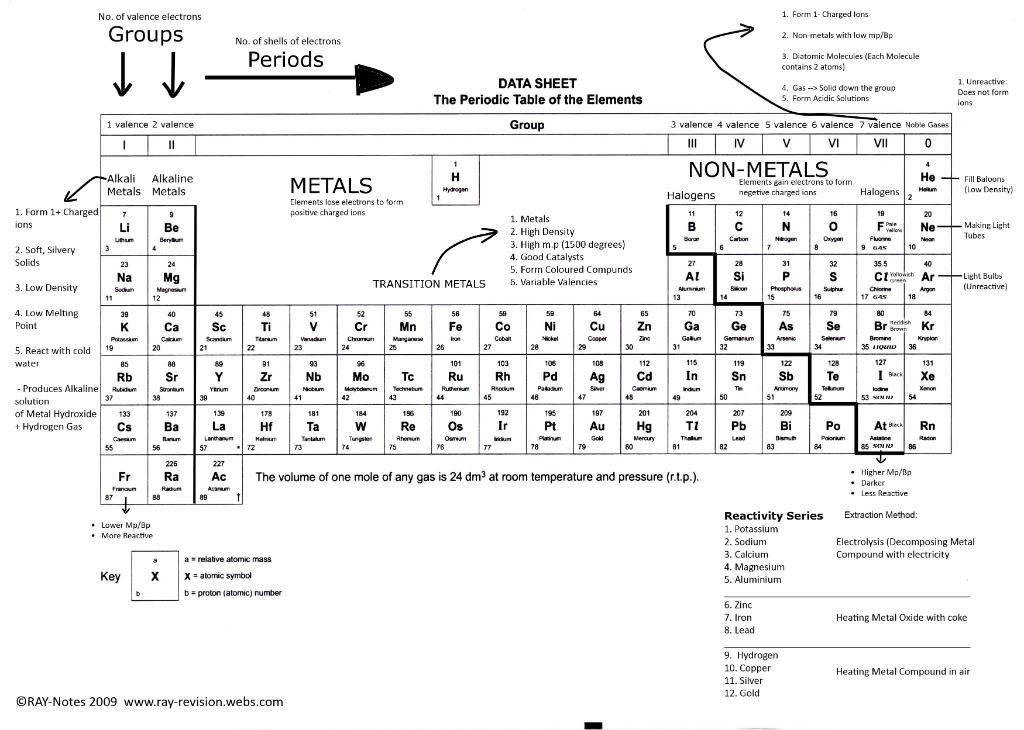
(This is the best of what I could fit. I suggest to use your own periodic table instead :P)
- -Main-group elements- Groups I to 0
- -Alkali Metals- Group I
- -Halogens- Group VII (non-metals)
- -Noble gases- Group 0 (very unreactive)
- -Transition elements- The block of elements between Group II and III
- -The broadest distinction in the table is metals and non-metals. Non-metals are on the right of the thick line while the metals on the left side of the thick line.
- -A metal is an element that does conduct electricity, is malleable and ductile.
- -A non-metal is an element that doesn't conduct electricity and isn't malleable or ductile.
- -A metalloid is an element that have some features of a metal and some features of a non-metal.
- The difference between Metals and non-metals.
Metals
|
Non-Metals
|
They are usually solids at rtp except mercury which is liquid at rtp.
They have high mp and bp usually
|
They are usually solids or gases at rtp except bromine which is a
liquid at rtp.
They have low mp and bp often.
|
They are usually hard and have high density
|
Non-metals are softer than metals usually. They have low densities
usually.
|
All metals are good conductors of electricity.
|
Poor conductors of electricity
|
Malleable and ductile
|
Brittle
|
Grey in colour except gold and sliver, can be polished
|
Vary in colour, dull (when solid)
|
Sonorous
|
Not sonorous
|
Trends in the Periodic Table
- -Elements in the same group (vertical columns of elements) have the similar chemical properties and physical properties.
- -Elements in the same group have the same number of electrons in their outershell.
- -For main-group elements, the number of the group is the number of electrons in the outershell. For e.g chlorine is in Group VII so it has 7 electrons in its outershell.
- -The period (rows of elements) number tell us the number of shells in the element. Hydrogen in period 1 has 1 shell for e.g.
- -The atomic size of an atom increases down the group (as the number of shells increase) but decreases across a group since the number of electrons in the last orbit increases hence increasing the attractive force between electrons and protons (-ve and +ve) decreasing the size of the atom as a result.
- -Elements become more metallic (ability to lose electrons) down a group and less metallic across a period since the electrons in the last orbit increases so gaining electrons is much easier than losing them all.
- -In metal groups (like group I and group II) the reactivity of the elements increases as you go down the group.
- The most reactive metal is Caesium since Francium is radioactive (metals in Group I in more reactive than the metals in Group II)
- In the group of non-metals, the reactivity of the non-metals increase up the group
- The most reactive non-metal is Fluorine in Group VII.
litty
ReplyDeleteMay I have a clearer picture of your periodic picture pls ? I find it rlly helpful but I cant quite see the words clearly
ReplyDelete